rs_opw_kinematics/lib.rs
1//! Rust implementation of inverse and forward kinematic solutions for six-axis industrial robots
2//! with a parallel base and spherical wrist
3//!
4//! This work builds upon the 2014 paper titled _An Analytical Solution of the Inverse Kinematics Problem of Industrial
5//! Serial Manipulators with an Ortho-parallel Basis and a Spherical Wrist_, authored by Mathias Brandstötter, Arthur
6//! Angerer, and Michael Hofbaur. The paper is available on [ResearchGate](https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Mathias-Brandstoetter/publication/264212870_An_Analytical_Solution_of_the_Inverse_Kinematics_Problem_of_Industrial_Serial_Manipulators_with_an_Ortho-parallel_Basis_and_a_Spherical_Wrist/links/53d2417e0cf2a7fbb2e98b09/An-Analytical-Solution-of-the-Inverse-Kinematics-Problem-of-Industrial-Serial-Manipulators-with-an-Ortho-parallel-Basis-and-a-Spherical-Wrist.pdf).
7//! Additionally, it draws inspiration from a similar C++ project,
8//! [Jmeyer1292/opw_kinematics](https://github.com/Jmeyer1292/opw_kinematics), which served as a reference
9//! implementation for generating data for the test suite. This documentation also incorporates the robot diagram
10//! from that project.
11//!
12//! # Features
13//!
14//! - All returned solutions are valid, normalized, and cross-checked with forward kinematics.
15//! - Joint angles can be checked against constraints, ensuring only compliant solutions are returned.
16//! - To generate a trajectory of the robot (sequence of poses), it is possible to use "previous joint positions" as
17//! additional input.
18//! - If the previous joint positions are provided, the solutions are sorted by proximity to them (closest first).
19//! It is also possible to prioritize proximity to the center of constraints.
20//! - For kinematic singularity at J5 = 0° or J5 = ±180° positions, this solver provides reasonable J4 and J6
21//! values close to the previous positions of these joints (and not arbitrary ones that may result in a large jerk
22//! of the real robot).
23//! - Jacobian, torques, and velocities
24//! - The robot can be equipped with the tool and placed on the base, planning for the desired location and orientation
25//! of the tool center point (TCP) rather than any part of the robot.
26//! - Experimental support for parameter extraction from URDF.
27//!
28//! # Parameters
29//!
30//! This library uses seven kinematic parameters (_a1, a2, b, c1, c2, c3_, and _c4_). This solver assumes that the arm is
31//! at zero when all joints stick straight up in the air, as seen in the image below. It also assumes that all
32//! rotations are positive about the base axis of the robot. No other setup is required.
33//!
34//! 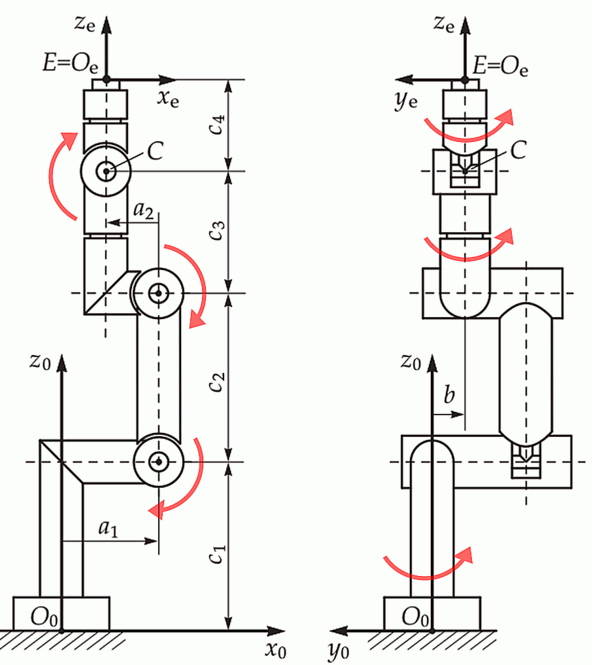
35//!
36//! To use the library, fill out an `opw_kinematics::Parameters` data structure.
37//!
38//! ## Examples
39//!
40//! The following examples demonstrate various functionalities provided by this crate:
41//!
42//! - **basic.rs**: Basic inverse and forward kinematics, including handling of singularities.
43//! - **constraints.rs**: Limiting the rotation range of robot joints.
44//! - **jacobian.rs**: Calculating Jacobian matrices for kinematic analysis.
45//! - **parallelogram.rs**: Supporting robotic arms with a parallelogram mechanism.
46//! - **tool_and_base.rs**: Configuring robots with a tool attachment and positioning on a specified base.
47//! - **frame.rs**: Using frames, a foundational concept in robotic programming for managing coordinates.
48//! - **complete_visible_robot.rs**: Constructing a complete robot with both shape and kinematics, including visualization.
49
50
51
52pub mod parameters;
53pub mod parameters_robots;
54
55#[cfg(feature = "allow_filesystem")]
56pub mod parameters_from_file;
57
58#[path = "utils/utils.rs"]
59pub mod utils;
60pub mod kinematic_traits;
61pub mod kinematics_impl;
62
63pub mod constraints;
64
65pub mod tool;
66
67pub mod frame;
68
69pub mod parallelogram;
70
71pub mod jacobian;
72
73#[cfg(feature = "allow_filesystem")]
74pub mod urdf;
75#[cfg(feature = "allow_filesystem")]
76pub mod parameter_error;
77
78#[cfg(feature = "allow_filesystem")]
79#[path = "utils/simplify_joint_name.rs"]
80mod simplify_joint_name;
81
82#[cfg(feature = "collisions")]
83pub mod collisions;
84
85#[cfg(feature = "stroke_planning")]
86#[path = "path_plan/cartesian.rs"]
87pub mod cartesian;
88
89#[cfg(feature = "collisions")]
90pub mod kinematics_with_shape;
91
92#[cfg(feature = "allow_filesystem")]
93#[path = "utils/read_trimesh.rs"]
94pub mod read_trimesh;
95
96#[path = "visualize/visualization.rs"]
97#[cfg(feature = "visualization")]
98pub mod visualization;
99
100#[path = "visualize/camera_controller.rs"]
101#[cfg(feature = "visualization")]
102mod camera_controller;
103
104#[cfg(feature = "stroke_planning")]
105#[path = "path_plan/rrt.rs"]
106pub mod rrt;
107
108#[cfg(feature = "stroke_planning")]
109#[path = "path_plan/rrt_to.rs"]
110mod rrt_to;
111
112#[cfg(test)]
113#[cfg(feature = "allow_filesystem")]
114mod tests;
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135